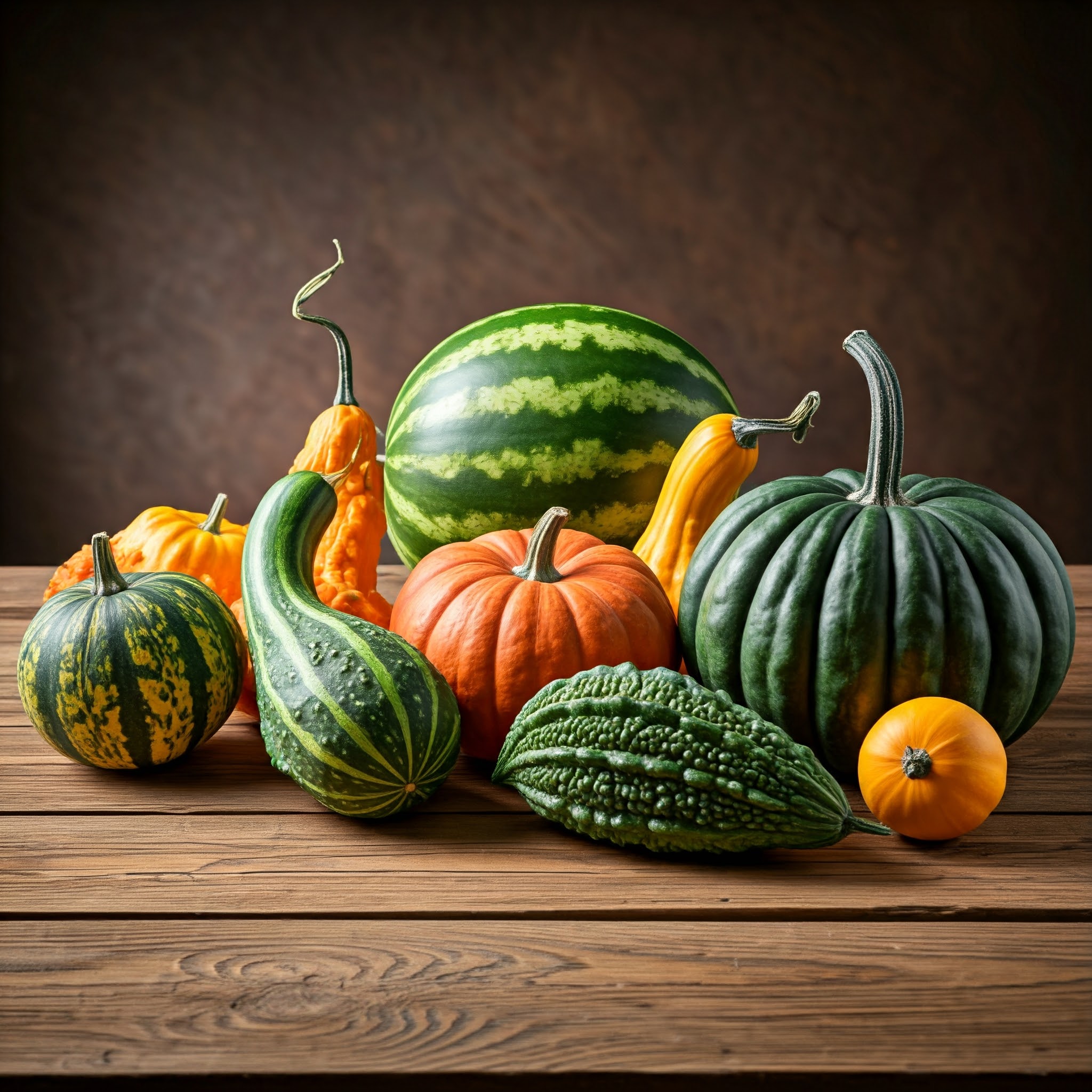
The Gourd Family: A Nutritious Treasure Trove
The gourd family, scientifically known as Cucurbitaceae, is a diverse group of flowering plants that have been cultivated for centuries for their edible fruits and seeds. These plants are characterized by their vine-like growth habits, large, lobed leaves, and unisexual flowers. The fruits, commonly referred to as gourds, vary widely in size, shape, color, and taste, and are used in a variety of culinary applications.
Popular Members of the Gourd Family in India
India is home to a rich diversity of gourd varieties, each with its own unique flavor profile and nutritional benefits. Here are some of the most popular members of the gourd family in India:
1. Bottle Gourd (Lagenaria siceraria):
Common Indian names: Lauki, Dudhi, Sorakkai
Description: Bottle gourd is a versatile vegetable with a long, cylindrical shape and a smooth, pale green skin. It has a mild, slightly sweet flavor and a high water content.
Uses: Commonly used in Indian curries, soups, stews, and stir-fries. It is also used to make juices and desserts.
2. Bitter Gourd (Momordica charantia):
Common Indian names: Karela, Bitter melon, Pavakkai
Description: Bitter gourd is a small, warty fruit with a bright green or yellow color. It has a bitter taste, which is often balanced by the addition of spices and sweeteners.
Uses: Bitter gourd is prized for its medicinal properties and is used in traditional Ayurvedic medicine to treat diabetes, digestive disorders, and skin conditions. It is also used in curries, stir-fries, and pickles.
3. Ivy Gourd (Coccinia grandis):
Common Indian names: Tendli, Kovakka
Description: Ivy gourd is a small, round fruit with a bright green or yellow color. It has a slightly bitter taste and a crisp texture.
Uses: Ivy gourd is often used in curries, stir-fries, and pickles. It is also used in traditional medicine to treat various ailments.
4. Ridge Gourd (Luffa acutangula):
Common Indian names: Tore, Peetha, Beeta
Description: Ridge gourd is a long, cylindrical fruit with ridges running along its length. It has a mild, slightly bitter taste and a crisp texture.
Uses: Ridge gourd is commonly used in curries, stir-fries, and pickles. It is also used in traditional medicine to treat digestive disorders and skin conditions.
5. Snake Gourd (Trichosanthes anguina):
Common Indian names: Padwal, Patol
Description: Snake gourd is a long, slender fruit with a bright green color. It has a mild, slightly sweet taste and a crisp texture.
Uses: Snake gourd is commonly used in curries, stir-fries, and soups. It is also used in traditional medicine to treat digestive disorders and skin conditions.
6. Sponge Gourd (Luffa cylindrica):
Common Indian names: Galka
Description: Sponge gourd is a long, cylindrical fruit with a rough, fibrous exterior. It has a mild, slightly bitter taste and a spongy texture.
Uses: Sponge gourd is often used in curries, stir-fries, and soups. It is also used in traditional medicine to treat digestive disorders and skin conditions.
7. Ash Gourd (Benincasa hispida):
Common Indian names: Petha, Kumara
Description: Ash gourd is a large, round fruit with a white or pale green color. It has a mild, slightly sweet taste and a crisp texture.
Uses: Ash gourd is commonly used in desserts, jellies, and preserves. It is also used in traditional medicine to treat digestive disorders and skin conditions.
8. Pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo):
Common Indian names: Kaddu, Kochu
Description: Pumpkin is a large, round fruit with a vibrant orange color. It has a sweet, slightly nutty taste and a soft, fleshy texture.
Uses: Pumpkin is commonly used in pies, soups, stews, and curries. It is also used in traditional medicine to treat digestive disorders and skin conditions.
9. Squash (Cucurbita spp.):
Common Indian names: Kaddu, Kochu
Description: Squash is a general term for a variety of gourd-like fruits, including butternut squash, acorn squash, and spaghetti squash. They vary in size, shape, color, and taste.
Uses: Squash is commonly used in pies, soups, stews, and curries. It is also used in traditional medicine to treat digestive disorders and skin conditions.
10. Watermelon (Citrullus lanatus):
Common Indian names: Tarbooz, Kandali
Description: Watermelon is a large, round fruit with a dark green rind and a bright red flesh. It has a sweet, juicy taste and a high water content.
Uses: Watermelon is primarily consumed as a fresh fruit. It is also used in juices, smoothies, and salads.
Nutritional Benefits of Gourds
Gourds are packed with essential nutrients and antioxidants that offer numerous health benefits. They are a good source of vitamins A, C, and K, as well as minerals like potassium, magnesium, and iron. Gourds are also high in fiber, which promotes digestive health and helps regulate blood sugar levels.
Some of the specific health benefits associated with consuming gourds include:
Improved digestion: The high fiber content of gourds helps to promote regular bowel movements and prevent constipation.
Weight management: Gourds are low in calories and high in fiber, making them a great addition to a healthy diet.
Boosted immunity: The antioxidants in gourds help to protect the body from damage caused by free radicals, which can contribute to chronic diseases.
Heart health: Gourds are a good source of potassium, which helps to regulate blood pressure. They are also low in saturated fat and cholesterol.
Diabetes management: Some gourds, such as bitter gourd, have been shown to have hypoglycemic properties, which can help to regulate blood sugar levels.
Culinary Applications of Gourds
Gourds are incredibly versatile and can be used in a wide variety of dishes. Here are a few popular culinary applications:
Curries: Many Indian curries feature gourds as a key ingredient. They add a depth of flavor and texture to the dish.
Stir-fries: Gourds can be quickly stir-fried with other vegetables and protein sources for a healthy and delicious meal.
Soups and stews: Gourds can be added to soups and stews for a hearty and nutritious meal.
Pickles: Many gourds, such as bitter gourd and ridge gourd, can be pickled for a tangy and flavorful side dish.
Desserts: Some gourds, such as ash gourd, are used in traditional Indian desserts.
Growing Gourds in India
Gourds are relatively easy to grow in India, as they thrive in warm, humid climates. They can be grown in gardens, on trellises, or in containers. Here are a few tips for growing gourds in India:
Choose a sunny location: Gourds require at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight per day.
Prepare the soil: The soil should be well-draining and rich in organic matter.
Plant the seeds: Seeds can be sown directly into the soil or started indoors and transplanted later.
Water regularly: Gourds require regular watering, especially during hot, dry weather.
Support the vines: If growing on trellises, provide adequate support for the vines to climb.
Harvest at the right time: Gourds should be harvested when they are firm and ripe.
By incorporating gourds into your diet, you can enjoy a variety of delicious and nutritious meals while also reaping the numerous health benefits that these versatile vegetables offer.